NIA submitted public comments on DOE’s Notice of New Categorical Exclusion and Request for Comment (DOE-HQ-2025-0405). NIA welcomes DOE’s commitment to advancing the deployment of advanced reactor technologies and recognizes the potential for categorical exclusions (CatEx) under the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) to conserve agency and applicant resources and reduce unnecessary delays for advanced reactors. However, for these changes to be durable, the application of CatEx for advanced reactors must be clearly justified by detailed information, bounding conditions, and sufficient empirical environmental review data.
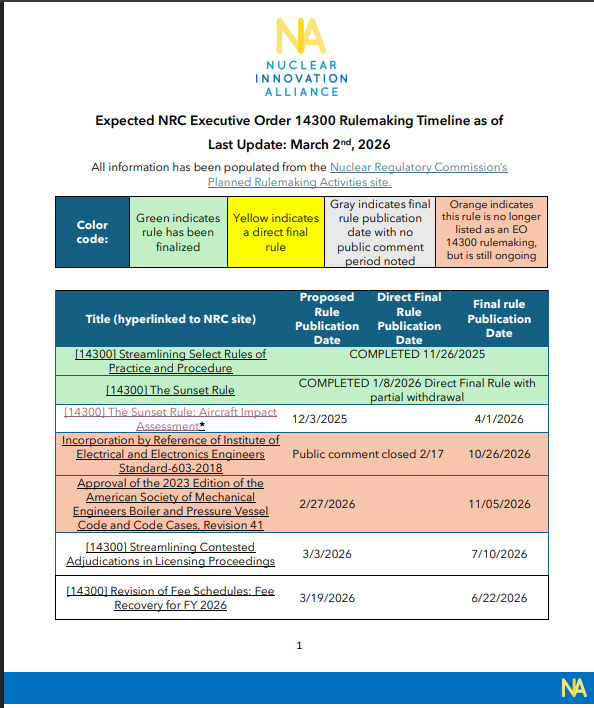
Expected NRC Executive Order 14300 Rulemaking Timeline
This NIA factsheet highlights the expected timeline of the NRC Executive Order 14300 Rulemaking. This timeline helps to provide a quick view of the individual rulemakings populated from the NRC website.
This factsheet was last updated in March 2026
The Nuclear Innovation Alliance hosted a publication webinar for our new U.S. Nuclear Energy Project Tracker created by Dr. James Richards, with speakers Kreshka Young of Dow, Katie Spence of Terrapower, Andrew Harmon of Natura Resources, James Richards of NIA, Judi Greenwald of NIA, and moderator Ben Finzel.
This resource complements the key indicators report NIA issued in October 2025 and highlights progress in each indicator for a project including site selection, licensing, commercial offtake, project team, and project funding.
To view the tracker click here: U.S. Nuclear Energy Project Tracker | NIA
On February 24, NIA analyst Zach Koshgarian testified before the Maryland State House of Representatives in support of HB970, which will change the current Renewable Energy Portfolio Standard to a Clean Energy Portfolio Standard and add nuclear energy as a Tier 1 renewable source.
To watch the hearing click here: ENT Committee Session, 2/24/2026

The Nuclear Innovation Alliance hosted a publication webinar for our new report "Right Sizing Reactors: Balancing trade-offs between economies of scale and volume," by Dr. Jessica Lovering with speakers Per Peterson of Kairos Power, Rita Baranwal of Radiant Nuclear, Robb Stewart of Alva Energy, Jessica Lovering of NIA, Judi Greenwald of NIA and moderator Ben Finzel.
If a country wants to build a lot of nuclear power fast, should the industry follow the mantra of bigger is better, or shift to focus on small modular reactors, or even microreactors, to follow the promise of factory fabrication? This new NIA report explores this question through economics literature and original analysis.
Click here to read the full report: Right-Sizing Reactors: Balancing trade-offs between economies of scale and volume | NIA
Right-Sizing Reactors: Balancing trade-offs between economies of scale and volume
If a country wants to build a lot of nuclear power fast, should the industry follow the mantra of bigger is better, or shift to focus on small modular reactors, or even microreactors, to follow the promise of factory fabrication? The new NIA report, “Right-Sizing Reactors: Balancing trade-offs between economies of scale and volume,” by Dr. Jessica Lovering explores this question through economics literature and original analysis.
As Dr. Lovering concludes in the report, there absolutely is evidence for economies of scale with nuclear reactors, but there is also a history of significant cost overruns due to the challenges of megaproject management. When other energy technologies are small and modular, we see numerous benefits including steeper cost reduction curves, faster deployment, and lower financial risk. But there are some potential obstacles to nuclear energy benefiting from the same attributes as these other so-called “granular” technologies (small and modular), particularly uncertainty around scaling regulations.
The challenge now is to create the enabling conditions that let customers choose the right reactor for their specific needs and market. Success requires coordinated public and private actions that support a diverse portfolio of reactor designs and sizes—backed by efficient demonstration programs, accessible financing, strong project development, committed customers, risk-sharing tools, and real order books. Crucially, these actions must empower vendors to rapidly apply lessons learned, improve designs and processes, and compete on cost and performance, regardless of reactor size. If industry, government, investors, and civil society build this enabling environment, we can unlock cost declines on the scale of what solar and wind achieved over the past few decades.
The Urgency of NRC Reform
This brief, authored by NIA President & CEO Judi Greenwald, connects the role of advanced nuclear energy in meeting climate and energy security goals with the urgent need for NRC reform to enable advanced nuclear energy. It outlines the short-, medium- and long-term NRC reforms that are necessary to achieve that goal. It provides recommendations for action by Congress and the NRC and highlights several of NIA's recommendations for improving licensing efficiency. NIA developed this brief to serve as a guide for policymakers, the NRC itself, and key stakeholders in considering and then taking action to ensure the NRC can successfully meet this moment.
This brief was last updated in January 2026
On January 7, 2026, Judi Greenwald testified before the U.S. House of Representatives Energy and Commerce Committee during an Energy subcommittee hearing on American Energy Dominance: Dawn of the New Nuclear Era. To watch the full hearing click here: NIA's Judi Greenwald's Testimony before House Energy and Commerce, Energy Subcommittee | NIA
On January 7, 2026, Judi Greenwald testified before the U.S. House of Representatives Energy and Commerce Committee during an Energy subcommittee hearing on American Energy Dominance: Dawn of the New Nuclear Era. To read Judi Greenwald's full written testimony, click here: NIA's Judi Greenwald's Written Testimony for House Energy and Commerce, Energy Subcommittee Meeting | NIA
Nuclear Innovation Bootcamp Impact Report
Since 2016, The Nuclear Innovation Bootcamp (NIB) has enhanced the careers of students and young professionals working or looking to work in the advanced nuclear energy sector. As the demand for experienced leadership, new ideas, and professional development in this field continues to grow, NIB will be an increasingly important recruitment pipeline for multi-disciplined, creative, and energetic young talent. Looking forward, NIB is embarking on the next phase of its development by focusing on three core initiatives:
- Strengthening its commitments to innovation education and increasing multi-disciplined talent in the nuclear energy sector
- Expanding its engagement with a broader range of communities and industries
- Recruiting talent from underrepresented disciplines and professions
NIB centers on the NIB participants and every year we continue to learn from our growing alumni
network made up of the 196 participants of our eight Bootcamps. The information in this report is largely
based on survey results and interviews from this group. We hope that you will find the information and
stories below as motivating as we do.